I am not supporting these, just stating that these have been available for a while, and the
following are simple searches from PubMed.
Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Apr 4. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02468.x. [Epub ahead of print]
Peri-implant bone formation and surface characteristics of rough surface zirconia implants manufactured by powder injection molding technique in rabbit tibiae.
Park YS, Cung SH, Shon WJ.
SourceDepartment of Oral Anatomy, Dental Research Institute and School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate osseointegration in rabbit tibiae and to investigate surface characteristics of novel zirconia implants made by powder injection molding (PIM) technique, using molds with and without roughened inner surfaces.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: A total of 20 rabbits received three types of external hex implants with identical geometry on the tibiae: machined titanium implants, PIM zirconia implants without mold etching, and PIM zirconia implants with mold etching. Surface characteristics of the three types of implant were evaluated. Removal torque tests and histomorphometric analyses were performed.
RESULTS: The roughness of PIM zirconia implants was higher than that of machined titanium implants. The PIM zirconia implants exhibited significantly higher bone-implant contact and removal torque values than the machined titanium implants (P < 0.001). The PIM zirconia implants using roughened mold showed significantly higher removal torque values than PIM zirconia implants without using roughened mold (P < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS: It is concluded that the osseointegration of PIM zirconia implant is promising and PIM using roughened mold etching technique can produce substantially rough surfaces on zirconia implants.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
PMID:22471790[PubMed - as supplied by publisher] Related citations
•
2.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012 Mar-Apr;27(2):352-8.
Osseointegration of zirconia implants with different surface characteristics: an evaluation in rabbits.
Hoffmann O, Angelov N, Zafiropoulos GG, Andreana S.
SourceDepartment of Periodontics, School of Dentistry, Loma Linda University, Loma Linda, CA, USA.
[email protected] Abstract
PURPOSE: Zirconia ceramics are a viable alternative to titanium for use as dental implants. However, the smooth surface of zirconia means that longer healing periods are needed to accomplish osseointegration compared to roughened titanium surfaces. Surface modifications can be used to increase the roughness of zirconia. The aim of this study was to assess histologically and compare the degree of early bone apposition around zirconia dental implants with sandblasted, sintered, or laser-modified surfaces to that seen around surface-modified titanium implants. Removal torque was also measured and compared.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ninety-six implants--24 each of four types (sintered zirconia, laser-modified zirconia, sandblasted zirconia, and acid-etched titanium)--were placed in 48 New Zealand White female rabbits. One implant was inserted in each distal femur. Half of the specimens were harvested at 6 or 12 weeks and processed for light microscopic analysis; the area of bone-to-implant contact was measured morphometrically. The other half were evaluated for removal torque at 6 and 12 weeks.
RESULTS: No statistically significant differences existed in bone apposition between the different surfaces at either time point. Differences in removal torque were significantly different between titanium and sandblasted zirconia and between sintered zirconia and sandblasted zirconia, with the first mentioned demonstrating a higher torque value at 6 weeks. At 12 weeks, the only significant difference in removal torque was between titanium and sandblasted zirconia, with titanium demonstrating the higher value.
CONCLUSION: Comparable rates of bone apposition in the zirconia and titanium implant surfaces at 6 and 12 weeks of healing were observed. Removal torque values were similar for all implants with a roughened surface.
PMID:22442775[PubMed - in process] Related citations
•
3.Acta Odontol Scand. 2012 Feb 27. [Epub ahead of print]
Effects of micromovement on the changes in stress distribution of partially stabilized zirconia (PS-ZrO(2)) dental implants and bridge during clenching: A three-dimensional finite element analysis.
Choi AH, Matinlinna J, Ben-Nissan B.
SourceDental Materials Science, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong , PR China.
Abstract
Abstract Objective. This investigation aims to evaluate the changes in stress magnitudes and distributions on Partially Stabilized Zirconia (PS-ZrO(2)) dental implants and bridges and on the mandible caused by fibrous encapsulations during clenching. Materials and methods. Four 3.26 mm diameter PS-ZrO(2) dental implants with lengths of 12 mm were modelled and placed in the second premolar and first molar region on both sides of the mandible model. A rigid zirconia bridge with a thickness of 0.5 mm connects the PS-ZrO(2) dental implants placed in the second premolar and first molar. Four periodontal ligament (PDL) case studies were examined: PDL in the second premolars; PDL in the first molars; PDL in both the second premolars and first molars; and no PDL present. Results. The results reveal the magnitudes and distributions of stresses on the dental implants and connecting bridges were governed by the PDLs. A significant drop in stress levels were recorded when the PDL encapsulates the roots of the dental implants. Of the four PDL case studies, it was found that when the PDLs are present in both the second premolars and first molars the lowest stress magnitudes are generated. The analysis also revealed that, during the healing process after implant insertion and the result of fibrous encapsulation, the dental implant system will experience a varying amount of stress levels. Conclusion. This study was intended to produce more insight into the influence of the PDL on the changes in stress distribution on the dental implant system during clenching.
PMID:22364339[PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
The following 3 are for Z-system, the last one might be in-house.
Eur J Oral Implantol. 2010 Summer;3(2):111-20.
Immediate occlusal versus non-occlusal loading of single zirconia implants. A multicentre pragmatic randomised clinical trial.
Cannizzaro G, Torchio C, Felice P, Leone M, Esposito M.
Abstract
PURPOSE: To evaluate whether immediate non-occlusal loading of single zirconia implants could reduce early failures when compared to immediate occlusal loading.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Forty partially edentulous patients who received one single zirconia implant (Z-Systems) at least 10 mm long and 3.25 mm wide inserted with a torque of at least 35 Ncm were randomised to immediate occlusal or non-occlusal loading groups. All patients received provisional acrylic crowns the same day of implant placement. Provisional crowns were replaced after 4 to 5 months by definitive full ceramic crowns. Outcome measures were implant success, any complications and peri-implant marginal bone levels.
RESULTS: One year after loading, no patients had dropped out.
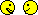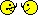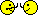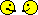
implants (12.5%) failed early: three occlusally loaded and two non-occlusally loaded. Three complications occurred, all after delivery of the definitive crowns: one crown fractured (occlusal loading),one had to be remade after debridement because of hyperplastic tissues (occlusal loading),and one crown decemented (nonocclusal loading). These differences were not statistically significant. Both groups gradually lost periimplant bone in a highly statistically significant way. One year after loading, patients subjected to non-occlusal loading lost an average of 0.7 mm of peri-implant bone versus 0.9 mm in the occlusal group. This difference in bone loss between groups was not statistically significant. There was an association between immediate post-extractive implants and implant failures (P=0.01). Four of the 10 immediate post-extractive implants (40%) failed versus one out of 30 delayed implants (3%).
CONCLUSIONS: The results of this study do not provide a conclusive answer to whether immediate non-occlusal loading may decrease implant failures. Immediately loaded zirconia implants placed in post-extractive sites had high failure rates.
PMID:20623036[PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Related citations
Publication Types, MeSH Terms, SubstancesPublication TypesMulticenter StudyRandomized Controlled TrialMeSH TermsAdolescentAdultAlveolar Bone Loss/etiologyChi-Square DistributionCrowns*Dental Implantation, Endosseous/adverse effectsDental Implantation, Endosseous/methods*Dental Implants, Single-Tooth*Dental PorcelainDental Prosthesis, Implant-Supported*Dental Restoration Failure*Dental Restoration, TemporaryDental Stress AnalysisFemaleHumansMaleMiddle AgedTime FactorsTooth Socket/surgery*Young AdultZirconiumSubstancesDental Porcelainzirconium oxideZirconium
•
2.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010 Jan-Feb;25(1):95-103.
Evaluation of stresses occurring on three different zirconia dental implants: three-dimensional finite element analysis.
Caglar A, Bal BT, Aydin C, Yilmaz H, Ozkan S.
SourceDepartment of Prosthodontics, Baskent University, Ankara, Turkey.
Abstract
PURPOSE: The aim of this study was to evaluate the von Mises, compressive, and tensile stresses occurring on three different zirconia dental implants and surrounding bone with three-dimensional finite element analysis. Materials and
METHODS: Three different zirconia implants (Z-Systems, Ziterion, and White-Sky),10 mm in length and 4 mm in diameter, and anterior maxillary bone were modeled using three-dimensional finite element analyses. Zirconia implants were placed into the maxillary left central incisor region. Loading was applied in horizontal and oblique axes (at angles of 90 and 30 degrees with respect to the implant long axes). Oblique loading was 178 N and horizontal loading was 25.5 N.
RESULTS: Under oblique loading, von Mises stresses for all implants were similar, and under horizontal loading conditions, the highest von Mises stress was found at the buccal and palatal neck region of the Ziterion implant (46.57 MPa). In cortical bone, the highest von Mises stresses were observed at the buccal region of the Z-Systems implant under oblique and horizontal loading conditions (26.65 MPa and 10.74 MPa, respectively). The highest compressive stresses were observed at the implant buccal neck region and cortical bone interface of the Z-Systems implant under oblique and horizontal loading conditions. For both loading conditions, the highest tensile stress values were observed at the implant palatal region and cortical bone interface of the Z-Systems implant.
CONCLUSION: The von Mises, compressive, and tensile stresses that occurred in cortical bone were higher than those observed in trabecular bone. Generally, the stresses in the Z-Systems implant were higher than in the other zirconia implants. The differences between the stress values occurring on the zirconia implants may be related to the different body and thread designs of these implants.
PMID:20209191[PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Related citations
MeSH Terms, SubstancesMeSH TermsAlveolar Process/physiologyCompressive StrengthComputer SimulationCrownsDental Implants*Dental ModelsDental Porcelain*Dental Stress Analysis*/methodsFinite Element AnalysisMaxillaStress, MechanicalTensile StrengthZirconiumSubstancesDental ImplantsDental Porcelainzirconium oxideZirconium
•
3.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2006 Dec;27 Suppl 1:69-72.
Soft and hard tissue response to zirconium dioxide dental implants--a clinical study in man.
Blaschke C, Volz U.
SourceZ-Systems Australasia, Auckland, New Zealand.
[email protected] Erratum in
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2007 Oct;28(5):iii.
Abstract
Titanium dental implants have been used successfully in implantology for more than 40 years. Recent research, however, suggests that titanium might have more side effects than previously believed. Zirconia ceramics have been employed in orthopaedic surgery for approximately 30 years and were recently introduced into dentistry as a metal replacement for crown and bridge work as well as implant abutments. Zirconium dioxide has been shown in both in vitro and in vivo studies to have desirable osseointegrative properties. This clinical study shows that dental implants made from zirconia are a feasible alternative to titanium dental implants. In addition to excellent cosmetic results, zirconia implants allow a degree of osseointegration and soft tissue response that is superior to titanium dental implants.
PMID:16892009[PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]



 implants (12.5%) failed early: three occlusally loaded and two non-occlusally loaded. Three complications occurred, all after delivery of the definitive crowns: one crown fractured (occlusal loading),one had to be remade after debridement because of hyperplastic tissues (occlusal loading),and one crown decemented (nonocclusal loading). These differences were not statistically significant. Both groups gradually lost periimplant bone in a highly statistically significant way. One year after loading, patients subjected to non-occlusal loading lost an average of 0.7 mm of peri-implant bone versus 0.9 mm in the occlusal group. This difference in bone loss between groups was not statistically significant. There was an association between immediate post-extractive implants and implant failures (P=0.01). Four of the 10 immediate post-extractive implants (40%) failed versus one out of 30 delayed implants (3%).
implants (12.5%) failed early: three occlusally loaded and two non-occlusally loaded. Three complications occurred, all after delivery of the definitive crowns: one crown fractured (occlusal loading),one had to be remade after debridement because of hyperplastic tissues (occlusal loading),and one crown decemented (nonocclusal loading). These differences were not statistically significant. Both groups gradually lost periimplant bone in a highly statistically significant way. One year after loading, patients subjected to non-occlusal loading lost an average of 0.7 mm of peri-implant bone versus 0.9 mm in the occlusal group. This difference in bone loss between groups was not statistically significant. There was an association between immediate post-extractive implants and implant failures (P=0.01). Four of the 10 immediate post-extractive implants (40%) failed versus one out of 30 delayed implants (3%).